
MAXIMA AND MINIMA
 |
MAXIMA AND MINIMA |
| Analysis | |
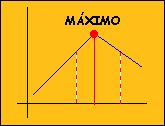
A function y=f(x) reaches a local MAXIMUM at a point xo when f(x)£f(xo) in the neighbourhood of xo
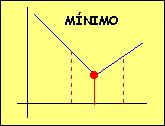
Similarly we can say that it reaches a local MINIMUM at a point xo when f(x)³f(xo) in the neighbourhood of xo
 |
 |
Let's see what happens when we are working with derived functions.
|
1. LOCAL MAXIMA AND MINIMA |
||||
|
A function y=f(x) reaches a local MAXIMUM at xo when f(x)£f(xo) in the neighbourhood of xo
Therefore:
|
||||
|
Similarly y=f(x) reaches a Local MINIMUM at xo when f(x)³f(xo) in the neighbourhood of xo
|
||||
|
||||
|
Now look carefully at the curves of the function y=f(x),its derivative y=f'(x) and the second derivative y=f''(x) in the window.
|
||||
| María José García Cebrian | ||
 |
||
| Spanish Ministry of Education. Year 2001 | ||

Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under a Creative Common License